Eulerian Video Magnification for Revealing Subtle Changes in the World
- paper website: https://people.csail.mit.edu/mrub/evm/
- related work: https://people.csail.mit.edu/mrub/vidmag/
- paper with code: https://paperswithcode.com/task/motion-magnification
- connected papers: https://www.connectedpapers.com/main/1ad1b8a6b365ff7011b7eac1dded748639ae972b/graph?utm_source=share_popup&utm_medium=copy_link&utm_campaign=share_graph
- youtube: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ONZcjs1Pjmk
- an english blog: https://hbenbel.github.io/blog/evm/
- a chinese blog: https://www.hahack.com/codes/eulerian-video-magnification/
What is the goal?
Combine spatial decomposition and temporal filtering to reveal color and motion changes for perceptually appealing visualization (artifact-free).
What is the idea?
EVM relies on the optical flow algorithm to estimate the motion between frames, assuming that changes in pixel intensity represent pixel motion, provided that the image brightness does not change and the motion is smooth.
What is the method?
- decompose the video into different spatial frequency bands.
- perform temporal filtering on each band.
- amplify the motion in each band.
- reconstruct the video.
| Property | Spatial Decomposition | Temporal Filtering |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | Separate the video into different spatial frequency bands. | Extract and amplify the motion in the temporal domain. |
| Key variable | (cutoff wavelength) | / (band-pass frequency range) |
| Method | Pyramid | Band-pass filter |
| Main role | Control motion at different scales (such as large range vibration and small detail changes) | Extract movement at a specific time frequency (e.g., heart rate, camera vibration) |
What does the 2D Fourier transform of an image do?
Originally, an image is a matrix of pixels in the spatial domain. Through Fourier Transform (FT), it becomes a combination of frequency planes (spectrum) with different weights in the frequency domain. Each plane represents a different spatial frequency. The high-frequency spectrum appears denser and represents the edges of objects.

What is spatial decomposition?
this method uses a Gaussian pyramid for color magnification and a Laplacian pyramid for motion magnification.
- Gaussian pyramid: It is a multi-scale representation of an image, where each level of the pyramid corresponds to a different spatial resolution. The image is downsampled and smoothed using Gaussian blur, which is achieved by convolving the image with a Gaussian kernel (convolution operation).
- Laplacian pyramid: It is a representation of the image in terms of the difference between the original image and the upsampled and smoothed version of the image in Gaussian pyramid (Laplacian of Gaussian operation). It captures the high-frequency details of the image.
What is frequency band?
Frequency band is a range of frequencies in the spectrum. There are 2 types of bands: spatial and temporal.
- Spatial bands relate to the variation of pixel intensity in space (width and height). High frequency represents fine details (edge), while low frequency represents smooth regions (background).
- Temporal bands relate to the variation of pixel intensity in time (frame rate). Frequency corresponds to the speed of motion.
Fourier transform and Band-pass filter can be used to isolate a specific frequency band. A demo of band-pass filter is shown below.

What is pyramid representation?
A pyramid of a video is a multi-scale representation of a video sequence, where each level of the pyramid corresponds to a different spatial or temporal resolution.
In pyramid representation of this method, as the level increases, the resolution of the image decreases, and the frequency information contained in it gradually changes from high frequency to low frequency. At the top of the pyramid is the lowest resolution image, which mainly contains low-frequency information.
What is temporal filtering?
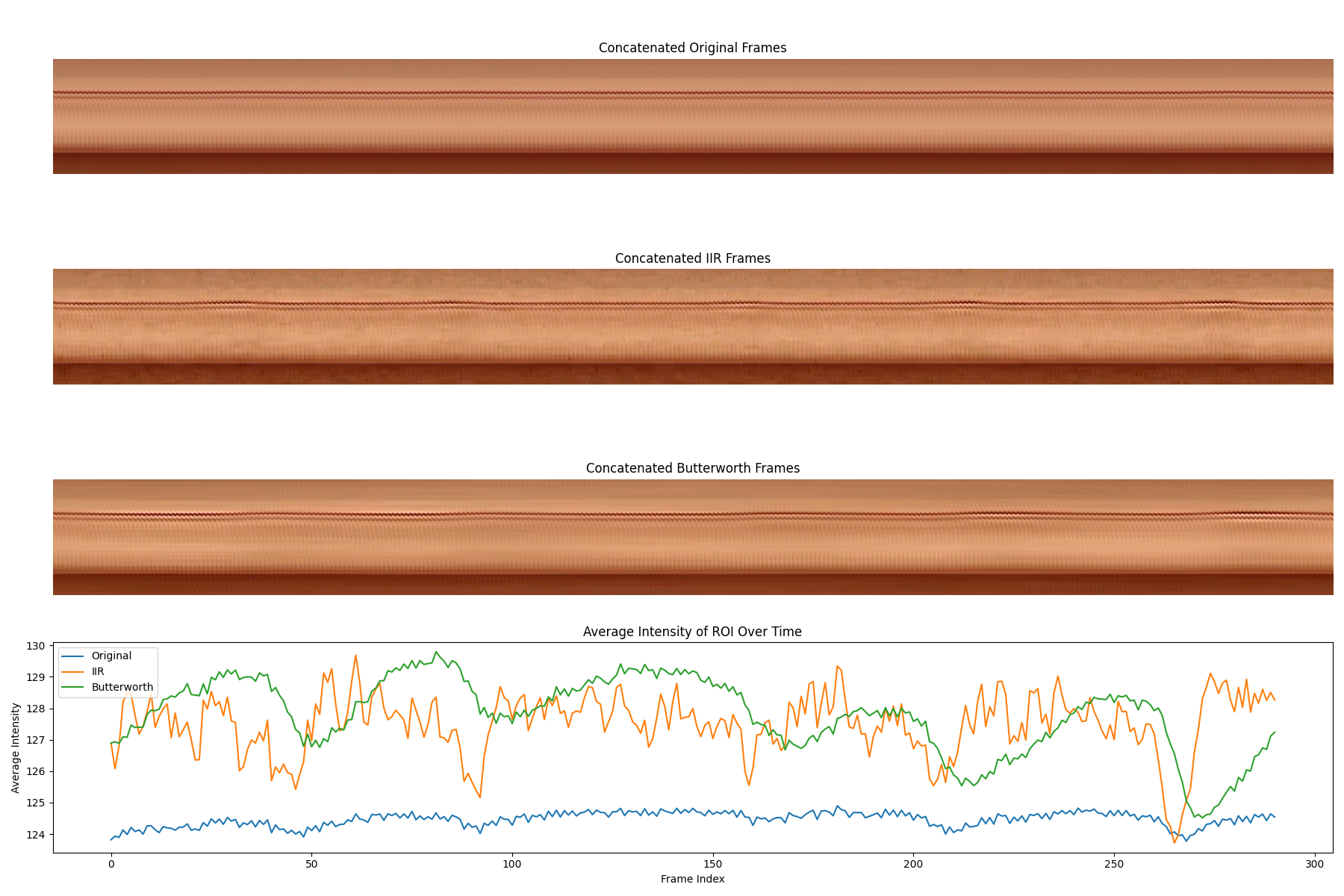
This method uses a Butterworth band-pass filter to amplify the motion in the temporal domain.
- Ideal band-pass filter: It allows a specific range of frequencies to pass through while blocking others. It is ideal in the sense that it has a sharp cutoff and no ripples in the passband or stopband. It is hard to implement in practice due to its infinite impulse response and non-causal nature.
- Butterworth filter and IIR (Infinite Impulse Response) filter: It is a type of filter that has a smooth rolloff in the frequency domain. It can be implemented using recursive formulas and is more practical for real-time applications.
What are passband and stopband in a filter?
The passband is the range of frequencies that are allowed to pass through the filter with minimal attenuation. The stopband is the range of frequencies that are blocked or attenuated by the filter.
What are spatial, temporal and frequency domain?
- Spatial domain (x,y,intensity(x,y)): The original representation of an image or video in terms of pixel values. It is the domain where the image is defined in terms of its spatial coordinates (width and height).
- Temporal domain (intensity(x,y,t),t): The domain where the video is defined in terms of time (frame rate). It captures the changes in pixel values over time.
- Frequency domain (u,v,magnitude(u,v)): The domain where the image or video is represented in terms of spatial or temporal frequencies. It provides insights into the frequency content of the signal, such as the presence of high or low frequencies.
How to amplify motion?
EVM achieves motion amplification through the following steps:
- Modeling: The motion is viewed as the product of the spatial gradient of the signal and the displacement in the time domain.
Assume that the initial intensity distribution of signal is f(x), small translation over time t is δ(t), and the observed signal is - Approximation: Taylor expansion linearized small shifts.
When the displacement δ(t) is small, the intensity change can be approximated by the first-order Taylor series expansion: - Processing: Time filter extracts the moving component of the target, amplifies and reconstructs the signal.
Decompose the displacement δ(t) in the frequency domain (such as Fourier transform), and the target frequency band is extracted through a band-pass filter:Apply the amplification factor α to the filtered displacement:
Reconstruct the amplified signal:
Where:
- : observed intensity at position x and time t.
- : intensity distribution of the signal, which can be represented as a (a set of) sinusoidal function(s).
- delta: displacement function over time t.
- derivative: spatial gradient of the signal.
- gamma: temporal attenuation factor of a filter for different frequency components.
- : different temporal spectral components of the displacement.
- alpha: amplification factor for the motion.
How to explain F3 and F4 in the paper?
- X-axis: represents spatial position (such as horizontal one-dimensional coordinates).
- Y-axis (or signal strength axis) : represents the light intensity value (such as brightness) of the signal.
- Timeline (implicit dimension) : In the model, time t is an implicit variable, not directly as a coordinate axis, but reflected by the time evolution of the signal. For example, the displacement function δ(t) describes the overall translation of the signal with time t, but the analysis usually fixed the spatial position xx and observed its brightness change with time (i.e., time series analysis).
What is first-order Taylor series expansion?
It is a linear approximation of a function around a specific point. It is used to estimate the value of a function near the point. The approximation is given by the first-order Taylor series expansion:
where is the function, is the function value at , is the derivative of the function at , and is the point of interest.
Why use sinusoidal function to estimate the image intensity?
It is the basic function in Fourier analysis. It captures the periodic nature of the intensity changes in the image.
What is spatial frequency ω (omega) and wavelength λ (lambda)?
They are in inverse relationship. High frequency has short wavelength, while low frequency has long wavelength. High frequency represents fine details (edge), while low frequency represents smooth regions (background).
In the multi-scale processing (spatial decomposition) of EVM, the amplification factor of each spatial frequency band k is adjusted:
What will motion magnification errors?
The difference between the estimated motion and the actual motion .
Why the lowpass1 and lowpass2 keep updating in the code?
Accumulate filter states to filter the video signal in the time domain, rather than depending only on the current/previous frame.
Why updating the filter equals to computing the temporal derivative?
The temporal derivative is the rate of change of a signal with respect to time. By updating the filter, the motion is estimated by the temporal changes in the signal.
Why r1 and r2 are used in the code?
They are the ratio of the current frame to the previous frame, controlling the response speed of the filter:
When r approaches 1, the filter responds faster to the input signal and is able to capture higher frequency changes.
When r approaches 0, the filter responds more slowly to the input signal and can only capture changes in lower frequencies.
A more academic explanation of above 2 questions would be the following.
What is a first-order digital lowpass filter?
Ask GPT
一阶数字低通滤波器(first-order digital lowpass filter)通常是 IIR滤波器(Infinite Impulse Response filter)的一种。
Ask GPT
传递函数(Transfer Function)是描述系统输入和输出之间关系的函数。在频域中,传递函数是输入信号和输出信号的傅里叶变换之间的比值。
对于一个线性时不变系统(LTI系统),传递函数 定义为输出信号的拉普拉斯变换 与输入信号的拉普拉斯变换 之间的比值:
其中:
是传递函数。
是输出信号的拉普拉斯变换。
是输入信号的拉普拉斯变换。
是复频域变量。
在离散时间系统中,传递函数通常用 变换表示:
其中:
是离散时间系统的传递函数。
是输出信号的 变换。
是输入信号的 变换。
是复频域变量。
Ask GPT
拉普拉斯变换(Laplace Transform)是一种数学变换方法,用于将一个函数从时间域转换到复频域。
对于一个时间域函数 ,其拉普拉斯变换 定义为:
其中:
- 是 的拉普拉斯变换。
- 是时间域函数。
- 是复频域变量,通常表示为 ,其中 和 是实数, 是虚数单位。
逆拉普拉斯变换用于将复频域函数 转换回时间域函数 ,其定义为:
其中:
- 是 的逆拉普拉斯变换。
- 是复频域函数。
- 是实数,使得积分路径位于 的所有奇点的右侧。
Ask GPT
Z变换(Z Transform)是一种数学变换方法,用于将一个离散时间序列从时间域转换到复频域。
对于一个离散时间序列 ,其Z变换 定义为:
其中:
- 是 的Z变换。
- 是离散时间序列。
- 是复频域变量,通常表示为 ,其中 是幅度, 是角频率, 是虚数单位。
It is a kind of "moving average" filter, which is used to smooth the signal and remove high-frequency noise. Given input signal and output signal , the first-order digital lowpass filter can be represented by the following difference equation:
where is the filter coefficient, which controls the amount of smoothing applied to the signal. A smaller value results in less smoothing, while a larger value results in more smoothing. EVM sets as motion frequency.
And its transfer function in the Z domain is:
where is the transfer function, is the output signal in the Z domain, and is the input signal in the Z domain.
Ask GPT
通过对差分方程进行Z变换,可以得到系统的传递函数。
对 进行Z变换:
对 进行Z变换:
对 进行Z变换:
将这些结果代入差分方程的Z变换中:
将所有 项移到方程的左边:
提取 :
解出传递函数 :
What is a first-order Butterworth lowpass filter?
Given a frequncy and a sampling rate , the first-order Butterworth lowpass filter can be represented by the following difference equation:
y[n] = \frac{-b[1] y[n-1] + a[0] x[n] + a[1] x[n-1]}{b[0]}$$. And its transfer function in the Z domain is: $$H(z) = \frac{Y(z)}{X(z)} = \frac{a[0] + a[1]z^{-1}}{b[0] + b[1]z^{-1}}
where is the transfer function, is the output signal in the Z domain, and is the input signal in the Z domain.
Ask GPT
对 进行Z变换:
对 进行Z变换:
对 进行Z变换:
对 进行Z变换:
将这些结果代入差分方程的Z变换中:
将所有 项移到方程的左边:
提取 :
解出传递函数 :
Why the output of these filters are shifted?
The output of these filters is shifted because the filters are causal and have a delay in their response. The shift is due to the time it takes for the filter to process the input signal and produce the output signal.
Ask GPT
相位响应(Phase Response)是描述滤波器对输入信号的相位变化的影响。它表示输入信号的每个频率分量在通过滤波器后,其相位发生了多少变化。相位响应在信号处理和滤波器设计中非常重要,因为它影响信号的时间特性和波形。
对于一个线性时不变系统(LTI系统),其传递函数 或 可以表示为复数形式:
或
其中:
或 是幅度响应(Magnitude Response),表示滤波器对不同频率分量的增益。
或 是相位响应,表示滤波器对不同频率分量的相位变化。
相位失真(Phase Distortion):如果滤波器的相位响应不是线性的,不同频率分量会经历不同的相位变化,导致信号波形的失真。这在音频处理和通信系统中尤其重要,因为相位失真会影响信号的保真度和清晰度。
群延迟(Group Delay):群延迟是相位响应的导数,表示信号的不同频率分量通过滤波器时的时间延迟。理想情况下,群延迟应该是常数,这样所有频率分量都经历相同的时间延迟,保持信号的波形不变。
